Reading Comprehension and English Language Learners in High School
English linguistic communication learners (ELLs) often take issues mastering science, math, or social studies concepts considering they cannot comprehend the textbooks for these subjects. ELLs at all levels of English proficiency, and literacy, will benefit from explicit teaching of comprehension skills along with other skills.
Examples of comprehension skills that tin can be taught and practical to all reading situations include:
- Summarizing
- Sequencing
- Inferencing
- Comparing and contrasting
- Drawing conclusions
- Self-questioning
- Problem-solving
- Relating groundwork knowledge
- Distinguishing betwixt fact and opinion
- Finding the main thought, important facts, and supporting details
These skills are particularly important for comprehending what is generally known every bit information reading or expository reading.
Related Resources
For more than information, run into our related articles and classroom videos:
- Reading Comprehension Strategies for English language Learners
- Reading 101 for English Language Learners
- Classroom Video Library: ELL Instruction
Why reading comprehension skills are peculiarly important for ELLs
ELL students will all the same need a lot of vocabulary development and teaching of comprehension strategies even if they:
- have been mainstreamed after some bilingual instruction;
- are being pulled out for English every bit a Second Language or Sheltered English instruction; and/or
- take been assessed as English language proficient but yous know that they still need boosted help with language, reading, and writing.
Hither is a way of thinking about the support your ELLs will need:
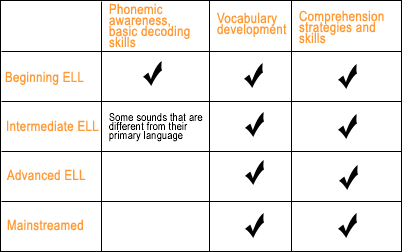
Classroom strategies: Steps for explicitly educational activity comprehension skills
The following steps are useful for all students. Nonetheless, these demand to exist complemented with the additional steps beneath to ensure comprehension for ELLs.
- Innovate the comprehension strategy or skill (encounter above list) through examples. Discuss how, when, where, and why the strategy or skills are used. For example: contrast main idea with details, fact with opinion, good summaries with poor summaries.
- Have students volunteer additional examples to dissimilarity and discuss.
- Label, define, model, and explicate the strategy or skill. For case, afterward listing four facts virtually a healthy nutrition and four opinions virtually what is good to consume, label 1 list as facts and the other listing as opinions.
- Give students opportunities to practice using the strategy with a peer as they apply it to a short, simple paragraph from a scientific discipline text or whatsoever expository text.
- Debrief with the whole grade to ask students to share how they practical the strategy or skill.
Additional steps for ELLs
- Identify vocabulary words that yous call back might be difficult for students to understand when they read the text. Write ELL-friendly definitions for each - that is, simple, brief definitions ELLs can hands sympathise.
- Model think-alouds. For example: verbalize a confusing point or show how yous employ a strategy to encompass something. "This sounds very confusing to me. I better read this judgement once again."
- Demonstrate fix-upwardly strategies. For case: I need to recall virtually this. Let me rethink what was happening. Possibly I'll reread this. I'll read alee for a moment.
- Partner ELLs with more dominant English language speakers and enquire each student to take a plow reading and thinking aloud with curt passages.
- After working with partners successfully, inquire ELLs to practice independently by using a checklist such as the following. Be certain to explain all the terms and model each.
While I was reading, how did I do?
| Skill I used | Not very much | A little fleck | Much of the time | All of the time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blending | ||||
| Chunking | ||||
| Finding pregnant of new word | ||||
| Making mind movies every bit I read | ||||
| Rereading | ||||
| Reading ahead |
- Celebrate each ELLs' progress with recognition notes, praise, and/or form applause.
For advanced ELLs
When students' English proficiency and basic reading skills have increased, y'all can teach the post-obit steps non just to ELLs, merely to all students – because everyone will benefit.
- In pairs, have students survey the text and use an idea map to record the chief idea and details.
- Ask partners to read the text.
- Take partners restate the main idea and supporting details. At this point, they tin can add together to their idea map or brand necessary corrections.
- Then enquire students to reread the text and either develop their own questions (pretending to gear up a test for their partner) or write a brusk summary of what they merely read.
- After that, have partners check each other's work.
- Finally, partners can share their questions or summaries with other teams.
Other ideas
For building ELL comprehension
Teach students how to use these tools for informational or expository reading:
- Titles
- Headings
- Bold print
- Captions
- Side bars
- Maps
- Graphs
- Pictures
- Bullets
Ask students to use the following strategies to summarize (orally or in writing):
- Retell what yous read, but keep it short.
- Include simply important information.
- Get out out less important details.
- Apply cardinal words from the text.
Questioning ELLs later reading
Later on the ELLs and/or whole class have completed the reading comprehension activities above, you tin anchor or exam their comprehension with carefully crafted questions, taking care to employ elementary sentences and key vocabulary from the text they just read.
These questions can be at the:
- Literal level (Why do the leaves turn scarlet and yellow in the fall?)
- Interpretive level (Why do you call back information technology needs water?)
- Practical level (How much water are you going to give it? Why?)
References
Calderón, Thousand. & Fifty. Minaya-Rowe (2004). Expediting Comprehension for English Language Learners (ExC-ELL): Teachers Manual. Baltimore, Doc: Centre for Data-Driven Reform in Education, Johns Hopkins University.
Calderón, M. & Fifty. Minaya-Rowe (in press). Teaching Reading, Oral Language and Content to English language Language Learners - How ELLs Keep Step With Mainstream Students. Chiliad Oaks, CA: Corwin Press.
Echevarria, J., Vogt, One thousand. E., & Curt, D. J. (2000). Making content comprehensible for English language learners: The SIOP model. Needham Heights, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Reprints
You are welcome to impress copies or republish materials for not-commercial employ as long every bit credit is given to Colorín Colorado and the author(s). For commercial utilize, please contact [email protected]
Source: https://www.colorincolorado.org/article/reading-comprehension-skills-english-language-learners
0 Response to "Reading Comprehension and English Language Learners in High School"
Post a Comment